Smart Greenhouses: IoT Technologies for Controlled Environments
Smart Greenhouses: IoT Technologies for Controlled Environments:This article centers on exploring the potential of IoT in revolutionizing greenhouse management. It delves into how IoT remote monitoring solutions are continually altering the landscape of greenhouse operations, highlighting the myriad ways they introduce innovation and deliver newfound benefits to this critical sector of agriculture.
The Remarkable Benefits of IoT in Smart Greenhouses

In the contemporary era, technology has revolutionized nearly every sector, profoundly transforming our lifestyle and elevating our overall well-being. Agriculture, a pivotal component of our food production, has not been immune to this evolution. Confronted by challenges such as the need for increased yields, resource scarcity, and the impact of climate change on traditional farming practices, technology has emerged as a solution, ushering in a new era for agriculture. Among these advancements, IoT-enabled greenhouses play a significant role in reshaping the future of the agricultural industry.
This article centers on exploring the potential of IoT in revolutionizing greenhouse management. It delves into how IoT remote monitoring solutions are continually altering the landscape of greenhouse operations, highlighting the myriad ways they introduce innovation and deliver newfound benefits to this critical sector of agriculture.
The Role of IoT in the Greenhouse Market
In the greenhouse market, IoT technologies are revolutionizing agriculture. Precision agriculture benefits from real-time data on environmental conditions, empowering informed decision-making. Automated climate control ensures optimal growth conditions. Resource management sees efficiency gains through precise irrigation and fertilization schedules. IoT remote monitoring solutions and instant alerts via mobile apps enhance oversight and response to critical conditions. Data analytics, energy-efficient smart lighting, and integration with broader systems refine operations. Disease prevention leverages early detection and automated treatment. Security is strengthened with IoT-enabled surveillance and access control. Market trends include continuous integration of AI, machine learning, and blockchain for secure data management. Overall, IoT in greenhouses drives cost reduction, enhances productivity, and supports sustainable agriculture.
How Smart Greenhouses are Changing Agriculture?
Smart greenhouses are transforming agriculture by leveraging advanced technologies. These intelligent environments use sensors and automation to optimize conditions for plant growth, precisely controlling factors like climate, irrigation, and fertilization. The integration of remote monitoring and data analytics enables real-time decision-making, enhancing overall efficiency. Automated disease prevention measures contribute to improved crop health. Smart greenhouses play a pivotal role in modernizing agriculture, increasing productivity, and promoting sustainable practices by minimizing resource wastage and enabling precision farming.
Major Factors of Greenhouse Environmental Control
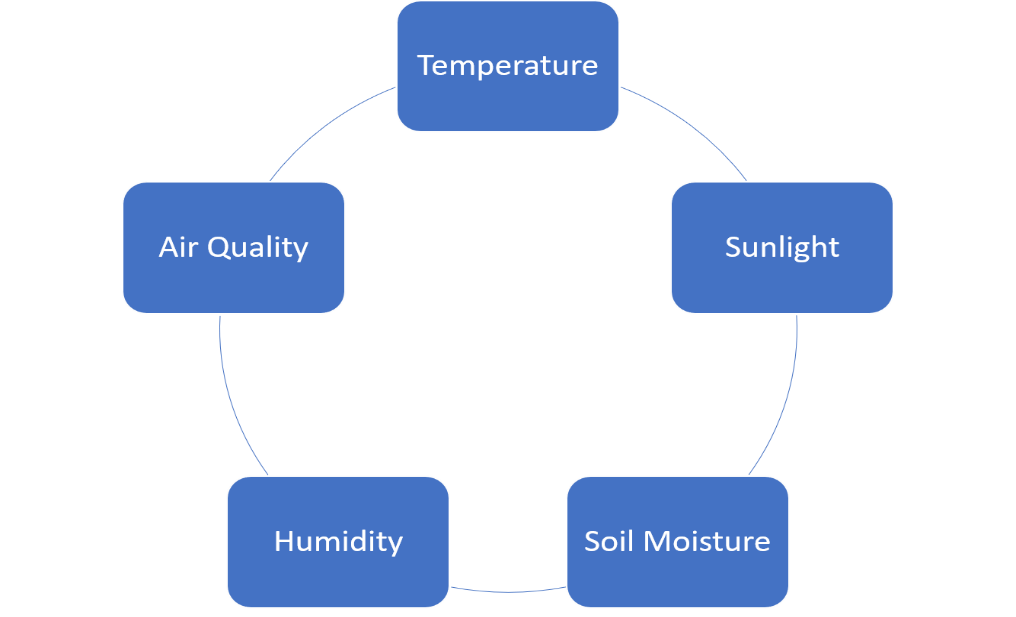
Temperature:
Temperature control is paramount in greenhouse environments, influencing the metabolic processes of plants. Different crops thrive within specific temperature ranges, and maintaining an optimal temperature is crucial for their growth and development. Greenhouses use heating systems during colder periods and ventilation or shading methods in warmer weather to ensure a consistent and favorable temperature for plants.
Air Quality:
Air quality is essential for plant health, directly affecting photosynthesis and respiration. Greenhouses maintain optimal air quality by implementing ventilation systems that facilitate the exchange of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. This ensures a balanced and conducive atmosphere for the growth of plants.
Sunlight:
Sunlight is the primary energy source for plants, driving the photosynthesis process. Controlling sunlight exposure is vital to meet the specific light requirements of different crops and prevent issues like sunburn or insufficient light for photosynthesis. Greenhouses utilize shading systems, movable curtains, and adjustable roof panels to manage sunlight penetration, ensuring an optimal and uniform distribution of light within the controlled environment.
Humidity:
Humidity levels play a critical role in plant transpiration, water uptake, and overall health. Maintaining optimal humidity is essential for preventing the development of fungal diseases and ensuring a proper water balance in plants. Greenhouses manage humidity through a combination of ventilation, heating, and cooling systems, with additional tools like dehumidifiers or misting systems to fine-tune humidity levels based on the specific needs of the cultivated plants.
Soil Moisture:
Soil moisture is a key factor in greenhouse environmental control, directly impacting plant growth and nutrient uptake. Greenhouses employ sensors and irrigation systems to monitor and maintain appropriate soil moisture levels. This ensures that plants receive adequate water for optimal growth, and nutrient availability is optimized for sustained health and productivity within the greenhouse environment.
Advantages of smart greenhouse
1 Optimize Micro-Climate Conditions for Ideal Growth
2 Improve Methods for Irrigation and Fertilization
3 Safeguard Against Infections and Disease Outbreaks
4 Prevent Thefts and Improve Security
1. Optimize Micro-Climate Conditions for Ideal Growth:
a. Greenhouse-Specific Climate Control:– Greenhouses demand precise control over temperature and humidity for diverse crops. IoT technologies facilitate continuous monitoring and automated adjustments tailored to the unique requirements of each crop within the greenhouse environment.
b. Light Optimization:– Supplementary artificial lighting is often crucial in greenhouses. IoT-connected systems dynamically adjust the intensity and duration of artificial light based on natural light conditions, ensuring that plants receive optimal light levels for their growth.
c. Greenhouse-Specific Data Analysis:– Machine learning algorithms, trained on greenhouse-specific data, consider factors such as structure and materials. This results in more accurate analysis and adaptive control, tailoring the environment to the specific conditions within the greenhouse.
2. Improve Methods for Irrigation and Fertilization:
a. Greenhouse-Specific Watering Needs:– Greenhouses exhibit variations in soil composition and water retention capacities. IoT sensors provide real-time data on soil moisture, enabling customized and efficient irrigation schedules that cater to the specific needs of plants within the greenhouse.
b. Tailored Fertilization for Greenhouse Crops:– Crops in greenhouses often have distinct nutrient requirements. IoT technologies analyze soil nutrient data and precisely deliver fertilizers, ensuring that greenhouse crops receive optimal nutrition for healthy and productive growth.
3. Safeguard Against Infections and Disease Outbreaks:
a. Closed Environment Management:– Greenhouses, being enclosed environments, are prone to disease spread. IoT technologies closely monitor plant health and promptly detect early signs of diseases. This enables a rapid response to prevent the widespread occurrence of infections within the confined space.
b. Quarantine Measures:– In case of disease detection, IoT systems aid in implementing quarantine measures, and isolating affected areas or plants. This containment strategy helps prevent the further spread of diseases within the greenhouse.
4. Prevent Thefts and Improve Security:
a. Greenhouse-Specific Security Challenges:– Greenhouses, often located in remote areas, face security challenges. IoT-connected surveillance systems and sensors provide an additional layer of security, addressing vulnerabilities in these isolated environments.
b. Protection of High-Value Crops:– High-value crops in greenhouses may be targets for theft. IoT security systems actively monitor and secure access to the greenhouse, safeguarding valuable crops from unauthorized access.
c. Integration with Greenhouse Management:– Security systems seamlessly integrate with overall greenhouse management. For instance, access control data can be linked with crop yield data, providing a comprehensive view of operations and potential vulnerabilities. This integrated approach enhances the overall security posture of the greenhouse.
In essence, the application of IoT technologies in Smart Greenhouses is not just about automation but also about tailoring the technology to the specific challenges and opportunities presented by the controlled environment of a greenhouse. The benefits include increased precision in resource management, early detection of issues, and improved security tailored to the unique conditions of greenhouse farming.
Terraconnect is a leading IoT development company that has been at the forefront of revolutionizing industries through its cutting-edge solutions. With a primary focus on IoT product development, hardware design, firmware development, and top-notch consulting services. Our commitment lies in fostering innovative and seamless IoT solutions, leveraging the latest advancements in technology. Connect with us for your IoT requirements https://terraconnect.io/contact-us/
Categories
Recent Articles

The Future of Water Management: TerraConnect Launches Terra M and Terra S in Kochi
Chaithanya

Experiencing the Future of Pool Management with Terra S
Chaithanya

The Smart Water Revolution: A Remote Village’s Journey with Terra M
Chaithanya